Having emerged during World War I in response to the regulation of prices and supplies, the black market burgeoned after the Bolshevik seizure of power. In 1918–1919, the Bolsheviks’ radical vision of socialism as an economy without capitalists or market mechanisms led to the closure of virtually all private shops. Until their re-legalization in 1921, in connection with the New Economic Policy, the distribution system consisted of a vast, bureaucratized, socialized network of state and cooperative outlets, and an equally vast underground trade. This illegal trade takes place in secret, or in the dark, hence the name “black market.” Because black-market trade occurs “off the books,” so to speak, it represents a whole sector of a country’s economy that cannot accurately be measured. Another form of government regulation that often leads to black-market trading is rationing. If individuals who want to buy more than the legal limit are willing to pay an extra price for this service, there will be merchants willing to ignore the government’s rationing limits to sell the goods for increased profit.

Black Market Exchange Rates

This is the case with unregistered firearms and cigarettes, which usually include a hefty local, state, or federal tax. Non-market activities, such as the production of household services or favors exchanged by friends and neighbors, fall into this category. Some black-market activities revolve around providing services that avoid taxation, depriving governments of revenue needed for public services. This includes unreported labor, where workers are paid in cash without payroll tax deductions, and under-the-table business transactions that bypass corporate income tax obligations. The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (IRS) estimates that the “tax gap”—the difference between taxes owed and taxes paid—was approximately $688 billion annually as of 2021, with a significant portion attributed to unreported income.
Black market activities of certain types can create clear and unambiguous harm to society, such as murder-for-hire services. Another financial incentive is the ability to exploit price controls and trade restrictions. When governments impose price ceilings—such as rent controls or caps on essential goods—black markets emerge to meet demand at higher, unregulated prices. High excise taxes on cigarettes in the United Kingdom (£6.06 per pack as of 2024) drive demand for untaxed alternatives, often smuggled from countries with lower taxes.
CBN Rates – Dollars To Nairas, Pounds To Nairas, Euros To Nairas, And Others

Meanwhile, across the pond, the dollar held steady against a host of other currencies, sitting at 97.99 on the index as investors braced themselves for the upcoming U.S. This report is the Fed’s go-to gauge for inflation, and it could influence the future course of monetary policy. Money markets are buzzing with an 85% chance of a U.S. rate cut next month, so it’s definitely a time for caution. There’s a kind of organization and disorganization to the black market, depending on certain demands or goods.
Black market competition can help keep prices in check, particularly for goods that are heavily taxed or subject to strict government controls. Second, the Soviet Union’s unstable legal environment makes it difficult to track changes over time. The basic juridical rubric for the black market was speculation (buying and reselling goods with the intention of making a profit), which was outlawed in every Soviet criminal code. It was applied sparingly and rather arbitrarily during the New Economic Policy, but Josef Stalin’s renewed assault on the private sector in the late 1920s created pressures for a formal redefinition. The law was finally softened in 1957 through the redefinition of petty speculation as a noncriminal offense, and then through the reduced prison sentence for criminal speculation in the 1960 RSFSR Criminal Code. Typically, black markets exist because of laws and regulations that ban certain products even though there is still demand for them.
Effects Of The Black Market
However, this can also be seen as the equivalent of legalizing crime in order to reduce the number of “official” criminal delicts—in other words, a concession that can be viewed negatively because of a perceived disappearing of moral values. Black markets can undermine legal businesses by offering similar goods and services without adhering to regulations or taxation, enabling them to sell at lower prices. This unfair competition can hurt legitimate businesses and discourage entrepreneurship. In extreme cases, such as during periods of political oppression, war, or economic collapse, black markets can serve as vital lifelines for individuals and communities. They can facilitate the trade of essential goods, help people preserve wealth, and even serve as a form of resistance against oppressive regimes.
Illegal Drugs
Southern women, especially those left behind by Confederate soldiers, demanded government action. Similar events also were reported in Richmond, Virginia; Mobile, Alabama; and Augusta, Georgia. Confederate states and cities sometimes responded with price controls or antimonopoly laws, which almost never succeeded. Cash remains a preferred medium of exchange for many illegal transactions due to its untraceable nature. Digital currencies like cryptocurrency have also become prevalent, offering anonymity for online black market activities.
Items Sold In Black Markets
- The risk of fraud, the threat of crime, and being saddled with counterfeit drugs or adulterated medicines, which is particularly problematic in the case of medications, are only some of the disadvantages of the black market.
- Illegal markets can take a toll on an economy because they are shadow markets where economic activity is not recorded and taxes are not paid.
- Often black market activities may benefit the direct participants in ways that are harmful to others, such as the buying and selling of stolen property.
- For decades, the black market has been a subject of intrigue, controversy, and concern.
- Once your account is confirmed, wire any amount from your personal bank to Dwolla from a lump sum or the estimated price of your purchase you have in mind.
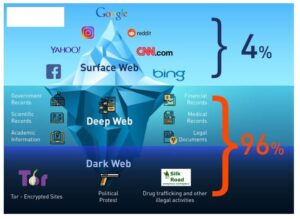
By offering viable and attractive legal alternatives, authorities can undercut the black market’s appeal and provide consumers with safe and ethical choices. With transactions increasingly occurring on the dark web, law enforcement faces greater challenges in combating these activities. Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have facilitated anonymous transactions, making it even more difficult to track and curb illegal operations within the black market.
Corporate Investigator Brandon Gregg Looks At How Bitcoins And Tor Make Anonymous Black Markets Tick

States engaged in total war or other large-scale, extended wars often impose restrictions on the use of critical resources that are needed for the war effort, such as food, gasoline, rubber, metal, etc., typically through rationing. Another in Britain was supplies from the U.S., intended only for use on U.S. army bases on British land, but leaked into the local native British black market. There is a big demand and a large market for these goods, despite strong laws designed to punish those who sell fake goods. The sale of counterfeit goods reduces the profits made by legitimate manufacturers and also undermines confidence in the market as a whole. Illegal markets can take a toll on an economy because they are shadow markets where economic activity is not recorded and taxes are not paid. It is often assumed that a country’s gross domestic product (GDP) is not accurate because it doesn’t account for any business activity conducted in underground markets.

Solutions To Black Markets
In Europe, the spotlight is also on inflation, with August’s flash consumer price index (CPI) data for Germany, France, Spain, and Italy set to drop today. Back in the foreign exchange market, the pound held steady against the euro, trading at €1.1561 as of the most recent update. With all these economic fireworks, investors are in for a rollercoaster ride as the day unfolds.
Black markets can also be attractive to sellers because black market products tend to sell at a premium and offer bumper profits. Because they are engaging in illegal activity and taking a risk, black market sellers can typically charge more than they would if they were selling a legal product. That premium acts as an incentive to sell on the black market, and it makes it harder to eliminate black market activity. By contrast, the black market refers to the buying and selling of illegal products or legal products that are purchased illegally. Black markets facilitate the exchange of a wide array of goods and services that are either illegal or transacted to avoid regulation.
By working collaboratively, governments can pool their resources and knowledge to develop comprehensive strategies for addressing the challenges posed by the black market on a global scale. For those involved in counterfeit goods or illegal financial transactions, penalties can include asset forfeiture and long-term imprisonment. Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations (RICO) Act, individuals engaged in organized black-market operations can face up to 20 years in prison per offense, along with the seizure of any assets derived from illegal activities. The illegal wildlife trade is another example, with products like ivory, rhino horn, and exotic pets being sold despite international bans. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) regulates the trade of endangered species, but black-market demand continues to fuel poaching and habitat destruction. Governments impose heavy fines and prison sentences for trafficking in protected species, with penalties varying by country.
Darknet Markets Generate Millions In Revenue Selling Stolen Personal Data, Supply Chain Study Finds
This includes the illegal movement of goods or people across borders to avoid taxes or immigration controls. It can involve items subject to high tariffs or quotas, such as cigarettes and alcohol, or even the smuggling of people, often in hazardous conditions. However, black markets can also attract organized criminal networks due to the high potential profits and the lack of regulatory oversight. These elements make the black market a complex and multifaceted aspect of the global economic system. Understanding this complexity is essential for creating effective policies and strategies to address the negative impacts of black markets while considering the economic realities that lead individuals to participate in them.
In situations where legal avenues fail to provide access to vital goods or services, people may face difficult decisions about supporting illicit activities. Striking a balance between satisfying immediate requirements and upholding ethical standards can be a formidable challenge. Addressing these dilemmas requires a multifaceted approach that includes not only providing legal alternatives but also addressing the underlying socioeconomic factors that drive individuals towards the black market. As an example of a black economy, a construction worker who is paid under the table will neither have taxes withheld, nor will the employer pay taxes on his earnings.